To fully grasp the concept of “what is MPLS”, it’s essential to understand how data moves within a network. When a person connects to a VoIP system or streams a video, data packets journey from one IP address to another. Routers utilize complex routing tables to dictate the path for each packet. This packet must be forwarded at every node until it reaches its final destination, causing potential delays. To address this, the MPLS network offers an accelerated alternative. This blog details the specifics of the MPLS network, addresses “What is MPLS?” and introduces MPLS VPNs.
What is MPLS? Exploring the Basics
To deeply comprehend the MPLS network, it’s crucial to first tackle the question, “What is MPLS?” MPLS, standing for Multiprotocol Label Switching, is a technique facilitating efficient data packet transfers over the internet. Contrary to traditional IP routing, where packets traverse extensively before reaching their destination, MPLS ensures packets head straight to their endpoint. This results in faster data packet transmission and a high-speed network.
MPLS Meaning: Understanding the Acronym
The MPLS meaning revolves around the label-based routing of packets over the internet. Instead of depending on a single protocol, the MPLS network uses various protocols to guide data packets based on their labels. This overlay system ensures a variety of data types are transmitted, no matter the originating protocol.
A distinctive aspect of MPLS is label switching. This mechanism enables system routers to form label-switched paths (LSPs) and pre-set routes for managing traffic within the MPLS network. Consequently, MPLS ensures superior transmission rates and a heightened Quality of Service (QoS) compared to traditional IP routing.
It is also important to remember that MPLS is not restricted to any one data transfer protocol. Because of its adaptability, it can be utilized with a variety of frameworks, demonstrating its protocol independence. This adaptability, pivotal to the MPLS meaning, ensures the technology remains relevant across multiple network architectures.
MPLS Network: A Comprehensive Overview
In the OSI seven-layer hierarchy, an MPLS network is Layer 2.5, which places it between Layer 2 (Data Link) and Layer 3 (Network). Layer 2 transports IP packets through basic LANs or direct WANs. Layer 3 is dedicated to global addressing and routing with IP protocols. MPLS, equipped with premium transport capabilities, sits strategically between these layers.
Upon entering the MPLS network, a data packet is designated a specific Class of Service (CoS). This label segment indicates the type of data within the packet, enabling routers to give priority to vital, real-time data like VoIP and video conferencing.
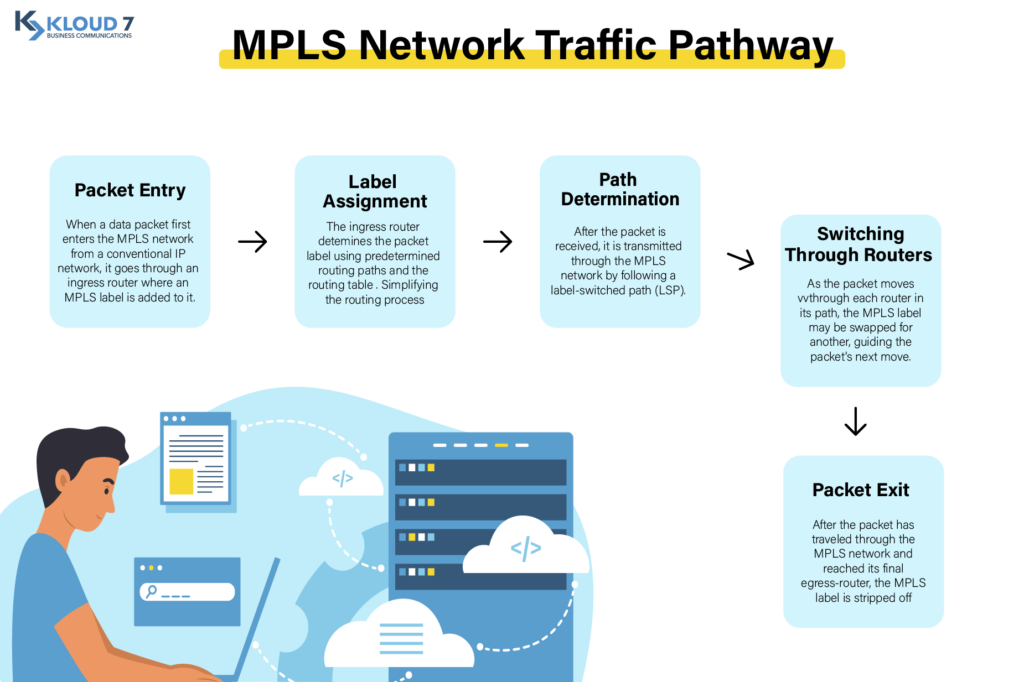
Steps of an MPLS Network Traffic Pathway
- Packet Entry: When a data packet first enters the MPLS network from a conventional IP network, it goes through an ingress router where an MPLS label is added to it. This label plays a vital role in routing the packet through the MPLS network, serving as both an identifying tag and a key to the entire process.
- Label Assignment: The ingress router determines the packet label using predetermined routing paths and the routing table. Simplifying the routing process, each label is a brief, predetermined value with a fixed length.
- Path Determination: After the packet is received, it is transmitted through the MPLS network by following a label-switched path (LSP). This path is a predetermined order of routers through which the packet will pass to ensure a quick and effective journey.
- Switching Through Routers: As the packet moves through each router in its path, the MPLS label may be swapped for another, guiding the packet’s next move. Label switching at each hop enables the packet to move through the network quickly.
- Packet Exit: After the packet has traveled through the MPLS network and reached its final egress router, the MPLS label is stripped off, and the packet is routed to its ultimate destination via the regular IP network.
This step-by-step pathway ensures that MPLS can offer faster routing than traditional IP networks, as it utilizes a predetermined path and simplified labels, reducing the decision-making time at each router.
MPLS VPN: Enhancing Network Security and Privacy
The prominence of the MPLS network has seen a significant rise in recent times, becoming a top choice for numerous organizations worldwide due to its adaptability and efficacy. A valuable extension to the MPLS network is the MPLS VPN. A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, offers a secure channel for transmitting data. In the context of the MPLS network, an MPLS VPN uses MPLS technology to protect data during transit. These virtual networks, superimposed on physical ones, emphasize multi-tenancy, virtualization, and modularity, thereby expanding the network’s scalability.
Final Thoughts
The MPLS network, represented by its innovative label-switching technique, optimizes the way data packets are routed, providing an enhanced, swift networking experience. By addressing the limitations of traditional IP routing and incorporating protective measures like MPLS VPN, this technological advancement is setting new standards in data communication. As our reliance on the internet keeps growing, tools like the MPLS network become essential in ensuring data is transferred efficiently, securely, and with high quality.




